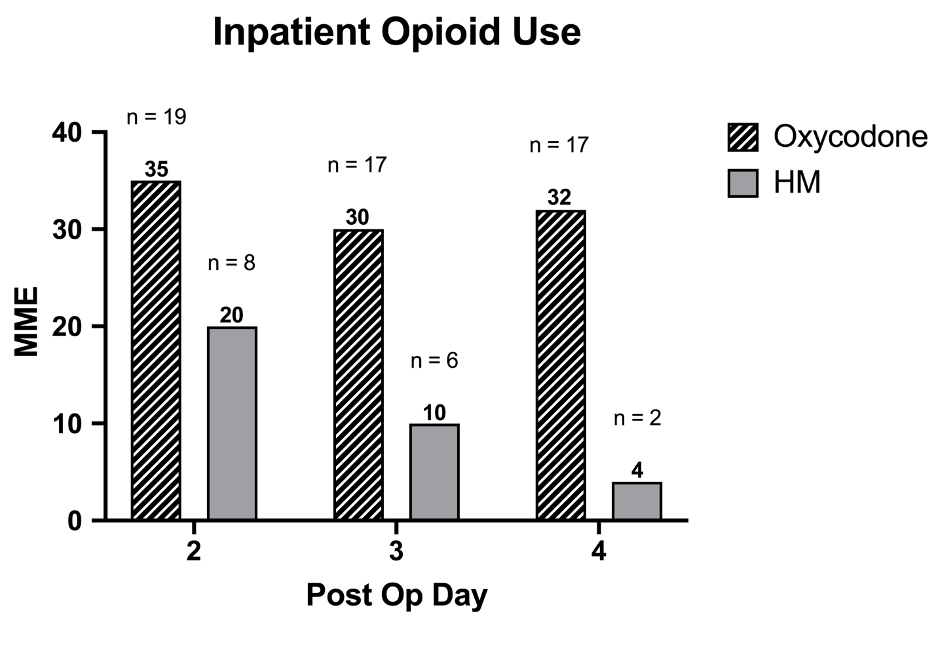Abstract
Introduction: There is sparse published literature on opioid use after gender affirming vaginoplasty (GAV). With creation of a neovagina and extensive external genital rearrangement, significant post-operative pain and opioid use would not be unexpected. We aimed to characterize inpatient opioid utilization after implementation of a standardized analgesia pathway.
Methods: An IRB-approved study was conducted on consecutive patients who underwent GAV by two surgeons from June 2020 to January 2021. Those on chronic narcotics (daily narcotic use ≥ 45 days pre-operatively) were excluded. As Patient-Controlled Analgesia was used POD0-1, data was only evaluated for POD 2-4. Opioid use was converted to morphine milligram equivalents (MME).
Results: 22 patients were included; 9 were robotic-assisted (41%). Median age 36 (range 19-79, IQR 30-48). BMI median 27, range 19-79 (IQR 30-48) Total MME was variable (median 104, IQR 45-164 MME) and equivalent to 30-110 oxycodone 5mg tablets. Robotic patients used less total MME (median 19 vs 154). 91% of patients received at least one dose of oral narcotic (n=20) while 55% used ≥1 intravenous (IV) dose of hydromorphone (n=12) . Urethral flaps were used in creation of labia minora in 9 patients (41%). These patients used much higher MME than those who underwent creation with penile skin flaps (median 52 vs 161 MME. There was no increased narcotic use with abdominal skin graft harvests (Median 60 vs 120 MME).
Conclusions: Our findings highlight the wide range of narcotic MME utilized by these patients. Oral narcotic use was utilized by more patients than IV. Patients who underwent the robotic approach used less total narcotic. Creation of the labia minora with urethral flaps was correlated with much higher narcotic use, while abdominal skin flap harvest was not. This may be due to urethral venous congestion and edema.