Abstract
Introduction and Objective: Prenatal hydronephrosis with concomitant hydroureter is an established risk factor for urinary tract infection (UTI); however, the minimum ureteral diameter for hydroureter is not well defined. We evaluated the definition of clinically significant hydroureter, its association with UTI and whether continuous antibiotic prophylaxis (CAP) impacted UTI risk.
Methods: Patients with prenatal hydronephrosis from seven centers were enrolled into the Society for Fetal Urology Hydronephrosis Registry from 2008-2020. Patients with ureteral measurement on ultrasound were included. Patients with ureterocele, ectopic ureter, neurogenic bladder, posterior urethral valves, horseshoe or solitary kidney, known ureteropelvic junction obstruction, or follow-up <1 month were excluded. Primary outcome was UTI. Analyses were performed using Cox regression.
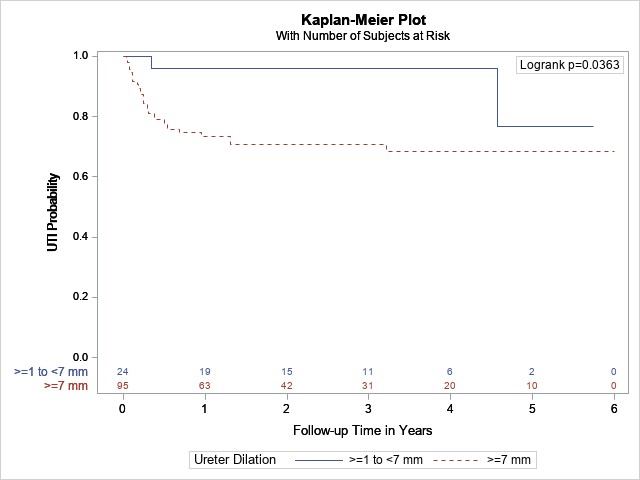
Results: Of 1406 enrollees, 237 met inclusion criteria. Hydroureter of 7 mm was a significant threshold to differentiate patients at higher UTI risk. Patients with ureters ≥7 mm had almost three times the risk of UTI adjusting for sex, circumcision, CAP, and hydronephrosis grade (HR = 2.7, 95% CI:1.1-6.5, p = 0.03). In patients without vesicoureteral reflux (VUR), ureteral dilation ≥7 mm corresponded with higher UTI risk compared to ureteral diameter <7 mm on multivariable analysis (HR = 4.6, 95% CI: 1.1-19.5, p = 0.04; Figure 1). Conversely, in patients with VUR, ureteral diameter ≥7 mm did not impact UTI risk (HR = 1.1, 95% CI:0.31-3.6, p =0.93). CAP was significantly protective against UTI for patients with hydroureter (HR = 0.50, 95% CI: 0.28-0.87, p = 0.01).
Conclusions: This is the first prospectively collected, multicenter study to show that prenatal hydronephrosis with hydroureter ≥7 mm identifies a high UTI risk group who would benefit from antibiotic prophylaxis. In contrast, patients with prenatal hydronephrosis and non-refluxing hydroureter <7 mm may be managed more conservatively.