Abstract
Objectives: Reductions in bothersome symptoms of overactive bladder (OAB) are reported to demonstrate improvement in clinical trials, often without interpreting meaningfulness to patients. In the 12-week phase 3 EMPOWUR trial, vibegron significantly reduced micturitions, urgency episodes, and urge urinary incontinence (UUI) episodes vs placebo (P<0.01, each). These analyses used an anchor-based approach to interpret the meaningfulness of symptom reduction with the patient global impression of change (PGI-C).
Methods: Median change from baseline (CFB) at week 12 in micturitions, urgency episodes, and UUI episodes was generated for each PGI-C category, pooled across treatments. Percentages of patients achieving these reductions in symptoms were determined.
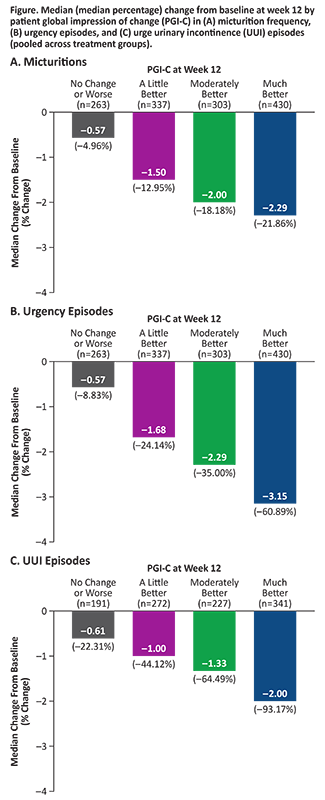
Results: Patients who experienced greater CFB at week 12 in each endpoint reported greater improvement in PGI-C. Median reductions from baseline in OAB endpoints pooled across treatment groups were higher than thresholds patients perceived as improved based on PGI-C: ≥15% reduction in micturitions (moderately better), ≥50% reduction in urgency episodes (much better), and ≥90% reduction in UUI episodes (much better; similar to ≥75% reduction seen in EMPOWUR [PGI-C: moderately better]) (Figure). Significantly more patients receiving vibegron vs placebo achieved these reductions (P<0.05, each).
Conclusion: Significantly more patients treated with vibegron vs placebo in EMPOWUR achieved meaningful reductions in micturitions and urgency/UUI episodes that were associated with patient-perceived improvement.
 1
1