Abstract
Radical cystectomy for persistent or invasive bladder cancer is a life saving, yet highly morbid procedure. Nationally and at Stanford, readmission rates in the 30 days after surgery persist at 30%, a rate significantly higher than other urologic procedures, and procedures in other fields of similar risk and complexity. This year, within the Clinical Effectiveness and Leadership Training program, a multidisciplinary team set out to lower the rate of readmissions following cystectomy.
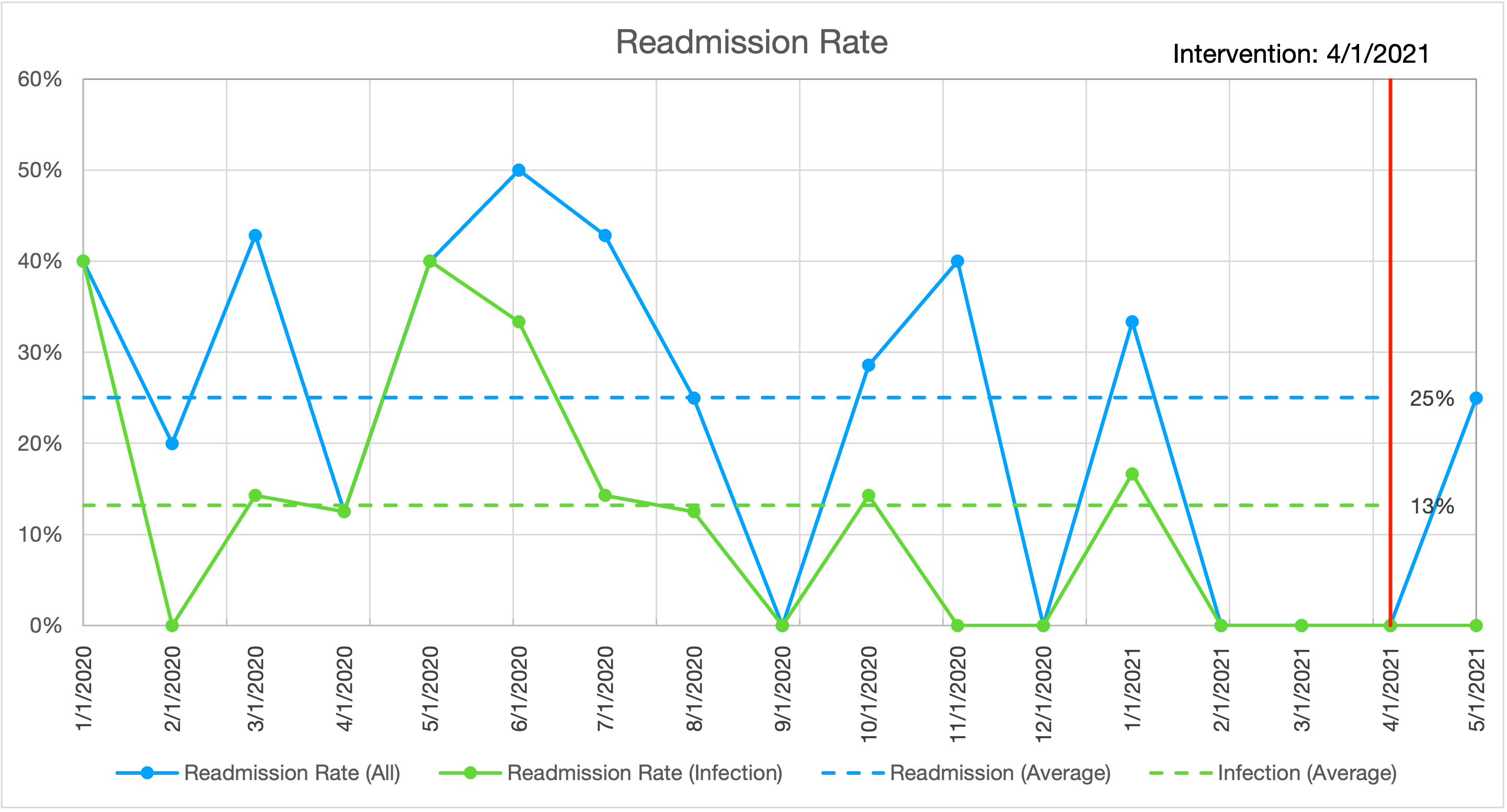
We measured the Stanford cystectomy readmission rate by examining National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) reports. When compared against billing and schedule data, we saw considerable mismatch. We thus performed a manual review of cystectomy procedures from the surgical schedule for 2018, 2019, and 2020. We identified 217 cases with a readmission rate of 28-32%. We categorized the readmissions and produced a Pareto chart. The principal cause of readmission was intraabdominal and urinary tract infection: 18-21%.
We designed a SMART goal: “To reduce the rate of readmission due to infection following radical cystectomy to 10% from the 18% by October 1, 2021. We performed a root cause analysis and literature search to design an ‘intervention bundle‘ to reduce readmissions due to infection:
Preoperative referral nutrition for supplements and optimization
Seamless MD education platform enrollment
Standardized teaching for post-operative inpatients
Remove ureteral stents by POD 4
Methenamine infection prophylaxis for 1 month
Outpatient care team coordination at discharge
Telehealth visit within 3 days of discharge, then weekly
We initiated our intervention on April 1, 2021.
In the 2 months since our ‘intervention bundle’ initiation, we have performed 7 radical cystectomies. 1 patient was admitted to an outside hospital with pain. No patients have been readmitted for infection. Process measures have also improved. Days to stent removal has improved from 21.3 days to 7.7 day (goal 4 days). Days to clinic follow-up on discharge improved from 6.3 days to 3.6 days (goal: 3 days).
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1AULFbKqHzjdgYbUSAwgDtv_WvvPL1zNj/view?usp=sharing